ubuntu chroot environment | What is chroot?
admin | March 3, 2025

What is chroot?
chroot (short for "change root") is a Unix/Linux command that changes the apparent root directory for a process and its children. This creates a "chroot jail", isolating processes from the rest of the system.
Why use chroot?
- Security – Restricts users or processes to a specific directory, preventing access to critical system files.
- Testing/Development – Run software in a controlled environment without affecting the main system.
- System Recovery – Mount a damaged system and fix it using a live Linux environment.
- SFTP/SSH Restriction – Limit SSH/SFTP users to their home directories for security.
Setup of chroot Environment
change to root user
sudo su -Add user
adduser <username>Setting up open-ssh
To install the OpenSSH server application, and related support files, use this command at a terminal prompt:
sudo apt install openssh-servernano /etc/ssh/sshd_configFind the line
#chrootDirectory #SubsystemThen change
Match User * ,!<username> ChrootDirectory %hnote: * means all user (wildcard) & ! means exclude
Change the ownership
chown root:root /home/<username Directory> chmod 755 /home/<username Directory>- Setup interactive shell for ssh chroot jail
First create bin folder into user directory
mkdir -p /home/<user>/binThen, copy main bin/bash into bin inter user
cp -v /bin/bash /home/<user>/bin/
Setup interactive session
ls -l /dev/{null,zero,stdin,stdout,stderr,random,tty}output:
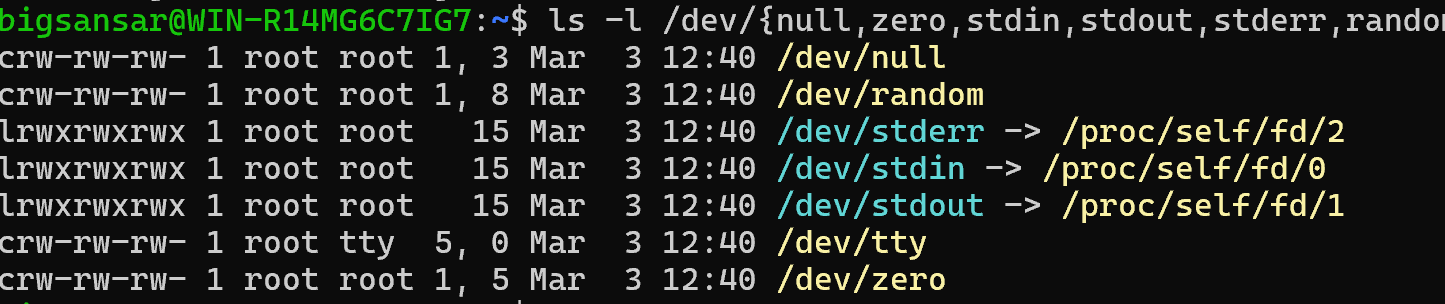
Then
mkdir -p /home/<username>/dev/ cd /home/<username>/dev/mknod -m 666 null c 1 3 mknod -m 666 tty c 5 0 mknod -m 666 zero c 1 5 mknod -m 666 random c 1 8
Identify bash required shared lib & lib64
ldd /bin/bashnote: see location of bash file
output
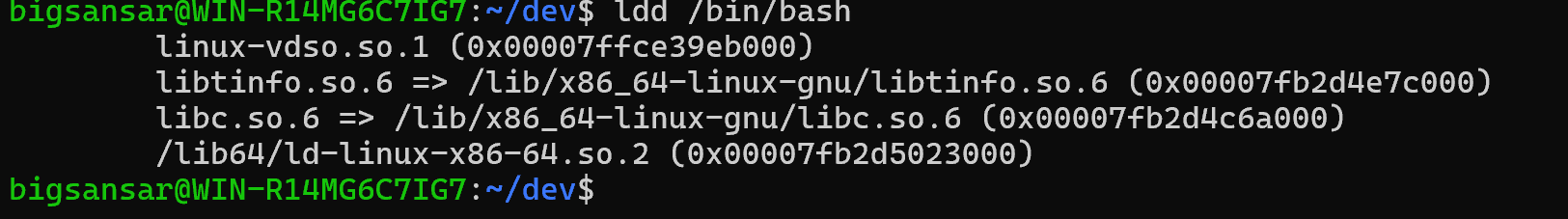
mkdir -p /home/<username>/lib mkdir -p /home/<username>/lib64 mkdir -p /home/<username>/lib/x86_64-linux-gnuThen copy all file related with bash file lib
cp -v /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/{filename} /home/<username>/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ cp -v /lib64/{filename} /home/<username>/lib64/Install few user command into bin folder
cp -v /bin/ls /home/<username>/bin/then try the step 7 for ls command
ldd /bin/ls
Some important cli for chroot
bash, ls , mkdir , chown, chmod
0 COMMENTS:
How to Install and Configure Apache on Ubuntu
2025-06-07 03:59:24.874882+00:00
Read Moreubuntu chroot environment | What is chroot?
2025-06-07 03:59:24.874882+00:00
Read MoreHow to Manage WiFi and Web Browsing in Linux Using the Terminal
2025-06-07 03:59:24.874882+00:00
Read MoreEssential Linux Commands for System Administration
2025-06-07 03:59:24.874882+00:00
Read MoreBeginner's Guide to Learning Ubuntu Server
2025-06-07 03:59:24.874882+00:00
Read More